Copiar el UsedRange de cada hoja en una hoja utilizando Microsoft Excel VBA en
En caso de que desee copiar el rango usado de cada hoja de trabajo en la hoja maestra, debe leer este artículo. Usaremos el código VBA para copiar los datos de cada hoja de trabajo y luego pegar en otra hoja sin sobrescribir .
La macro agregará una hoja con el nombre Maestro a su libro de trabajo y copiará las celdas de cada hoja de su libro de trabajo en esta hoja de trabajo .
La primera macro hace una copia normal y la segunda macro copia los valores. Los subs de la macro utilizan las funciones siguientes; la macro no funcionará sin las funciones.
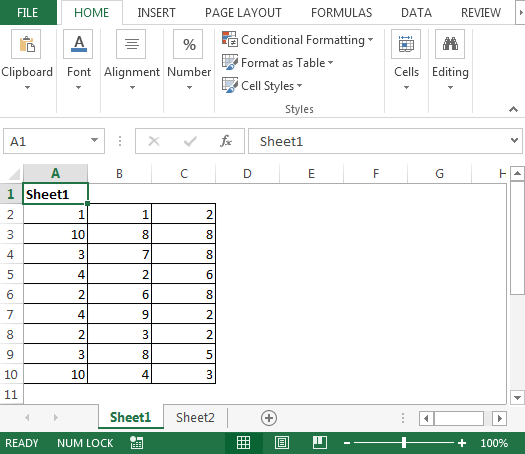
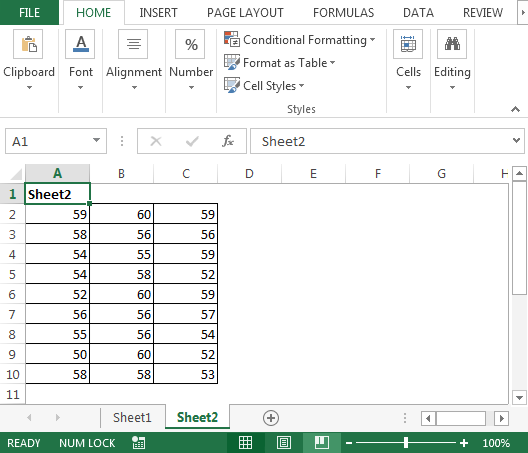
A continuación se muestra la instantánea de los datos de Sheet1 y Sheet2:
Necesitamos seguir los pasos a continuación para iniciar el editor de VB:
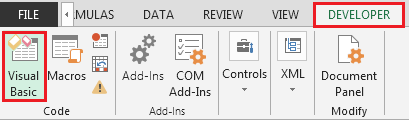
Haga clic en la pestaña Desarrollador Desde el grupo Código, seleccione Visual Basic
-
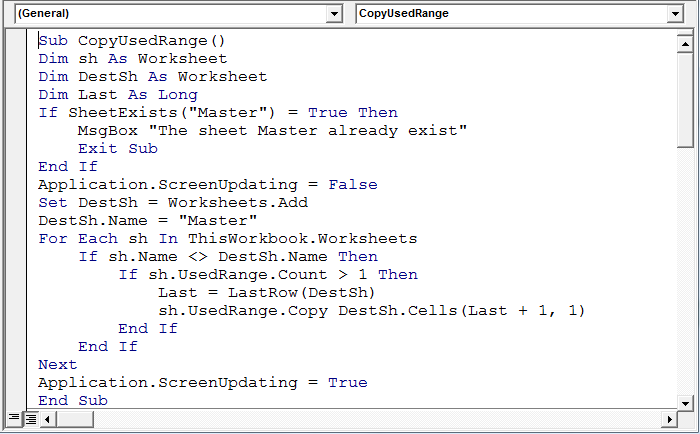
Copie el siguiente código en el módulo estándar
Sub CopyUsedRange()
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim DestSh As Worksheet
Dim Last As Long
If SheetExists("Master") = True Then
MsgBox "The sheet Master already exist"
Exit Sub
End If
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Set DestSh = Worksheets.Add
DestSh.Name = "Master"
For Each sh In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If sh.Name <> DestSh.Name Then
If sh.UsedRange.Count > 1 Then
Last = LastRow(DestSh)
sh.UsedRange.Copy DestSh.Cells(Last + 1, 1)
End If
End If
Next
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
Sub CopyUsedRangeValues()
Dim sh As Worksheet
Dim DestSh As Worksheet
Dim Last As Long
If SheetExists("Master") = True Then
MsgBox "The sheet Master already exist"
Exit Sub
End If
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Set DestSh = Worksheets.Add
DestSh.Name = "Master"
For Each sh In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If sh.Name <> DestSh.Name Then
If sh.UsedRange.Count > 1 Then
Last = LastRow(DestSh)
With sh.UsedRange
DestSh.Cells(Last + 1, 1).Resize(.Rows.Count, _
.Columns.Count).Value = .Value
End With
End If
End If
Next
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
Function LastRow(sh As Worksheet)
On Error Resume Next
LastRow = sh.Cells.Find(What:="*", _
After:=sh.Range("A1"), _
Lookat:=xlPart, _
LookIn:=xlFormulas, _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, _
MatchCase:=False).Row
On Error GoTo 0
End Function
Function Lastcol(sh As Worksheet)
On Error Resume Next
Lastcol = sh.Cells.Find(What:="*", _
After:=sh.Range("A1"), _
Lookat:=xlPart, _
LookIn:=xlFormulas, _
SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, _
MatchCase:=False).Column
On Error GoTo 0
End Function
Function SheetExists(SName As String, _
Optional ByVal WB As Workbook) As Boolean
On Error Resume Next
If WB Is Nothing Then Set WB = ThisWorkbook
SheetExists = CBool(Len(Sheets(SName).Name))
End Function
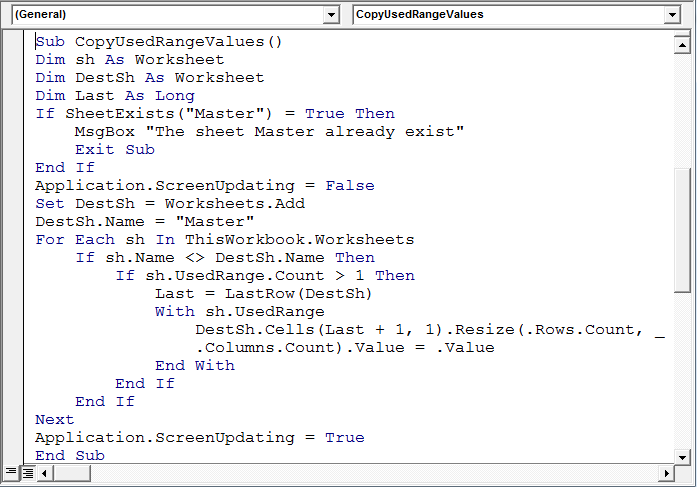
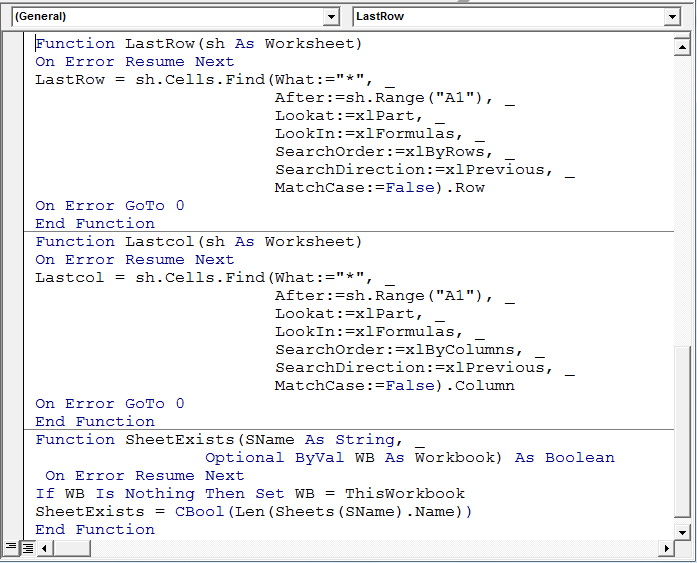
Ahora, el código macro está configurado; Ejecutaremos la macro «CopyUsedRange» e insertará una nueva hoja «Maestra» y copiará los datos de cada hoja.
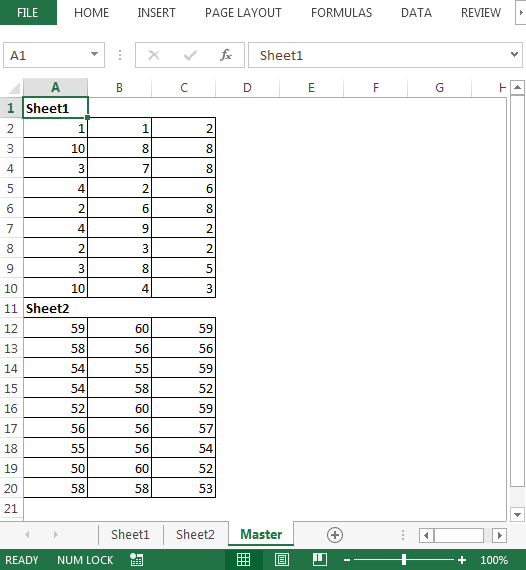
Conclusión: * Copiar datos de varias hojas es una tarea manual; sin embargo; con el código anterior, podemos consolidar datos con un solo clic en una macro.
Si te gustaron nuestros blogs, compártelo con tus amigos en Facebook. Y también puedes seguirnos en Twitter y Facebook.
Nos encantaría saber de usted, háganos saber cómo podemos mejorar, complementar o innovar nuestro trabajo y hacerlo mejor para usted. Escríbanos a [email protected]