lista de números aleatorios únicos utilizando VBA en Microsoft Excel generar
En este artículo, crearemos una función personalizada para generar una lista de números únicos y aleatorios entre los rangos especificados.
En este ejemplo, podemos ejecutar la macro haciendo clic en el botón «Enviar».
Antes de ejecutar la macro, tenemos que ingresar valores para cuatro parámetros. Hemos proporcionado el valor de límite inferior en la celda C12, el límite superior en la celda C13, el número de aleatorios únicos requeridos en la celda C14 y la dirección de destino donde se emitió se requiere en la celda C15.
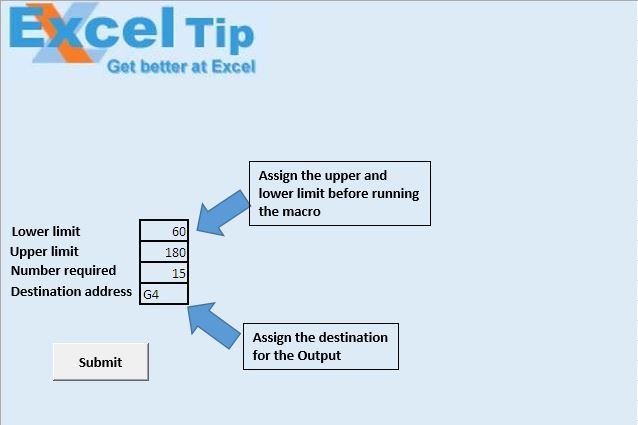
Explicación lógica
Hemos creado la función personalizada «UniqueRandomNumbers» para generar una lista de números únicos y aleatorios. Esta función toma el número requerido, el límite inferior y el límite superior como parámetros de entrada.
Hemos creado la macro «TestUniqueRandomNumbers» para llamar a la función personalizada «UniqueRandomNumbers». Esta macro se ejecuta haciendo clic en el botón «Enviar». Esta macro toma el valor de entrada del usuario del rango C12 a C15.
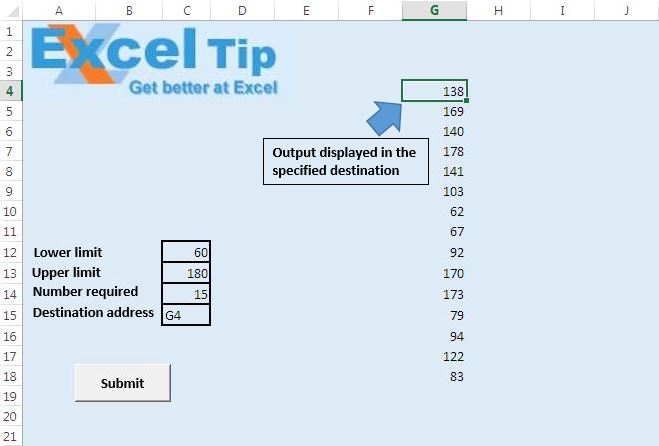
Explicación del código
i = CLng (Rnd () * (ULimit – LLimit) + LLimit)
La fórmula anterior se utiliza para crear el número aleatorio entre el límite superior e inferior definido. La función Rnd () crea un número aleatorio entre 0 y 1.
Rango (Selección, Selección.Desplazamiento (Contador – 1, 0)). Valor = _ Aplicación.Transponer (Lista de números aleatorios)
El código anterior se usa para transponer la salida de la matriz y asignar la salida al destino especificado.
Siga a continuación el código
Option Explicit
Function UniqueRandomNumbers(NumCount As Long, LLimit As Long, ULimit As Long) As Variant
'Declaring variables
Dim RandColl As Collection
Dim i As Long
Dim varTemp() As Long
'Validation check for the value specified by the user
If NumCount < 1 Then
UniqueRandomNumbers = "Number of unique random number required is less than 1"
Exit Function
End If
If LLimit > ULimit Then
UniqueRandomNumbers = "Specified lower limit is greater than specified upper limit"
Exit Function
End If
If NumCount > (ULimit - LLimit + 1) Then
UniqueRandomNumbers = "Number of required unique random number is greater than maximum number of unique number that can exists between lower limit and upper limit"
Exit Function
End If
'Creating new object of collection
Set RandColl = New Collection
Randomize
Do
On Error Resume Next
'Calculating the random number that exists between the lower and upper limit
i = CLng(Rnd() * (ULimit - LLimit) + LLimit)
'Inserting the unique random number in the collection
RandColl.Add i, CStr(i)
On Error GoTo 0
'Looping until collection have items equal to numCount
Loop Until RandColl.Count = NumCount
ReDim varTemp(1 To NumCount)
'Assigning value of the items in the collection to varTemp array
For i = 1 To NumCount
varTemp(i) = RandColl(i)
Next i
UniqueRandomNumbers = varTemp
Set RandColl = Nothing
Erase varTemp
End Function
Sub TestUniqueRandomNumbers()
'Declare variables
Dim RandomNumberList As Variant
Dim Counter As Long, LowerLimit As Long, UpperLimit As Long
Dim Address As String
'Getting the values input by the user
Counter = Range("C14").Value
LowerLimit = Range("C12").Value
UpperLimit = Range("C13").Value
Address = Range("C15").Value
'Calling custom function UniqueRandomNumbers
RandomNumberList = UniqueRandomNumbers(Counter, LowerLimit, UpperLimit)
'Selecting the destination
Range(Address).Select
'Assigning the value in the destination
Range(Selection, Selection.Offset(Counter - 1, 0)).Value = _
Application.Transpose(RandomNumberList)
End Sub
Si te gustó este blog, compártelo con tus amigos en Facebook y Facebook.
Nos encantaría saber de usted, háganos saber cómo podemos mejorar nuestro trabajo y hacerlo mejor para usted. Escríbanos a [email protected]